Insights From Our CEO: Are My Products Priced Correctly?
Welcome to our exclusive series of personal – and business – wealth management insights from Ajay Wasserman, Founder and CEO of the Fio Group. He is an expert business and wealth consultant to business owners and entrepreneurs to create long-term sustainable wealth.
In this article, I would like to explain to you how to price your product(s). When it comes to developing or manufacturing a new product, you need to factor in your margins before sending the product to market to prevent selling at a loss. This may seem complex and daunting, especially to avid entrepreneurs starting out in their industry. So, let’s recap the basics first.
What is a profit-mark-up?
Cost price: This is the amount of money it costs for you to have the product(s) manufactured. You must take into account tooling, all materials and any other elements required to get the product ready for market.
Wholesale price: This is the price you charge to sell your product to retailers. You’ll add a profit mark-up to the cost price so that you are making a profit from the sale. The % mark-up usually varies depending on the industry.
Retail price: This is the price at which stores will sell your product. The retail company will add its own profit mark-up to the wholesale price.
Gross, Operating, and Net Profit Margin
Gross profit margin, operating profit margin, and net profit margin are the three main margin analysis measures that are used to analyse a business’s income and gauge whether they are making a profit or a loss.
I have consulted many businesses that when we go into the marginal details of the product pricing, we realised that they are currently selling their product at a loss; in other words, they are essentially paying the client to buy their product.
-
Gross profit margin
The gross profit margin is the broadest of profit margins because it shows the profit of all income that the business makes after considering the cost of goods (COGS).
COGS include only direct costs associated with manufacturing or producing the products. Formula:
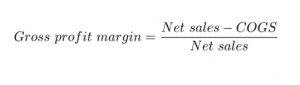
©Investopedia
COGS = Cost of Goods Sold
In a nutshell: the gross profit margin compares gross profit to total income, and the percentage reflects each rand that is retained as profit after paying for the cost of production.
-
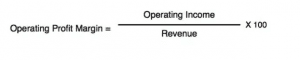
Operational profit margin
All businesses have a plethora of indirect costs such as research and development, marketing campaign expenses, general and administrative expenses, and depreciation and remuneration. The operating profit margin is the percentage of each rand that remains after payment for all operating business expenses. Formula:
©Investopedia
The operating profit margin is then calculated by dividing the operating profit by total income of the business. The operating profit figure indicated whether the business can manage all indirect costs, meaning that it shows the areas you’ve invested in to try and grow the business, e.g. marketing efforts.
In a nutshell: The operating profit margin shows whether or not a business can manage its direct expenses.
-
Net profit margin
Your net profit margin is calculated by analysing the last section of the income statement and the net earnings of a company after accounting for all expenses. Unlike gross profit margin, it takes into account interest and taxes. Formula:

©Investopedia
In a nutshell: Net profit highlights whether or not a business can manage its interest and tax payments. Interest payments can take several varieties such as the interest a business pays stakeholders on debt for capital securities. Net profit margin also includes any interest earned from investments (short and long-term).
Product pricing best practices
When it comes to product pricing you have to, firstly, make sure the value of your product justifies the price of your product. It’s best to book a business consultation with a professional marketing company. They will be able to take an in-depth look at your audience
Secondly, always make sure that you are not running at a marginal loss (which you’ll have determined by calculating and analysing your three profit margin metrics.)
Ensure that your cost to develop the product support to manufacture the product is lower than the price that you are selling it for there has to be a margin for your business to survive that profit will help you grow the business.
When you’re working on the pricing of your product for your market make sure that they can afford it first of all second key that they see the value in your product and that they are willing to purchase the product because of the value they will get in return. Once you nail that, you might have to test the market still in the future to make sure that your product pricing is still correct.
Connect with Ajay
Thank you for reading this article. I don’t want you to miss anything, so please subscribe to my YouTube channel, visit, and like, my Facebook page, connect with me on LinkedIn and follow me on Instagram and SoundCloud.



